The small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell. Fossil records indicate that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes somewhere between 15 to 2 billion years ago.
1Prepared by group 5.
/2000px-Celltypes.svg-58f4417b3df78cd3fcb40917.png)
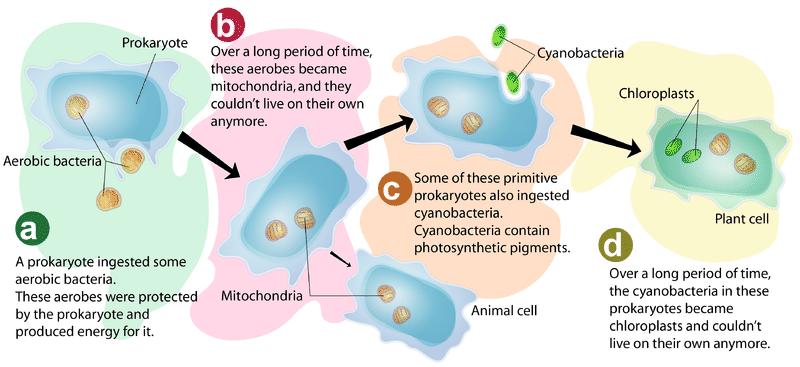
Evolution of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. It asserts that some of the organelles namely the mitochondria and chloroplast were originally smaller prokaryotic cells engulfed by larger prokaryotic cells. The strong energy constraints exerted on the organization of prokaryotic cells were a major factor of innovation at the origin of the evolution of this cell. A critical step in the evolution of eukaryotic cells was the acquisition of membrane-enclosed subcellular organelles allowing the development of the complexity characteristic of these cells.
The organelles are thought to have been acquired as a result of the association of prokaryotic cells with the ancestor of eukaryotes. Cells are divided into two main classes initially defined by whether they contain a nucleus. Structural proteins within.
Prokaryotes are the simplest organisms. Mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from prokaryotic organisms. How did a humble bacterium make this evolutionary leap from a simple prokaryotic cell to a more complex eukaryotic cell.
The Science Behind the Stories Jay H. Similarly any wastes produced within a prokaryotic cell can quickly move out. Download for free Report this document.
In conclusion the evolution of the eukaryotic cell was most likely by the way of the endosymbiotic theory with the original organelles of mitochondria and chloroplasts being prokaryotes that were incorporated into another prokaryotic or archean cell. Eukaryotic cells would go on to evolve into the diversity of. Typical prokaryote and eukaryote cells The complex eukaryotic cell ushered in a whole new era for life on Earth because these cells evolved into multicellular organisms.
The prokaryote domains are Bacteria and Archaea see Figure below. Their evolution is explained by endosymbiotic theory. Biology Mary Ann Clark Jung Choi Matthew Douglas.
Only cells that had mitochondria had sufficient energy resources to reach the complexity of the eukaryotic cell which is why there are no real intermediaries in the transition from prokaryotes to eukaryotes. But how did the eukaryotic cell itself evolve. Since prokaryotic cells are simpler than eukaryotic cells it is thought they came into existence first.
Table 11 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Characteristic Prokaryote Eukaryote Nucleus Absent. As life on Earth started to undergo evolution and become more complex the simpler type of cell called a prokaryote. Prepared by group 5 2.
The Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells from Prokaryotic Cells. Eukaryotic cells probably evolved about 2 billion years ago. Everythings an Argument with 2016 MLA Update University Andrea A Lunsford University John J Ruszkiewicz.
College Physics Raymond A. 1initially entered as undigested prey or as a parasite 2if photosynthetic-phloroplast or 3if oxygen requiring-mitochondria within the larger cell. RNA- Ribonucleic acid RNA is an acid that is present in all living cells its main role is to act as messenger and.
At 0150 μm in diameter prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells which have diameters ranging from 10100 μm Figure 4. The Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells 01. The third domain is Eukarya.
Evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The first eukaryotes evolved from ancestral prokaryotes by a process that involved membrane proliferation the loss of a cell wall the evolution of a cytoskeleton and the acquisition and evolution of organelles. This could have then been followed by a secondary engulfing event also by a prokaryote or perhaps a different kind of cell.
Eukaryotic cells origionated from symbiotic prokaryotic cell that is small prokaryotes living inside larger prokaryotic cells the small prokaryotic. Evidence supports the idea that eukaryotic cells are actually the descendents of separate prokaryotic cells that joined together in a symbiotic union. In fact the mitochondrion itself.
Home Documents Evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The answer seems to be. 1 page 251 words.
Prokaryotes are currently placed in two domains. How did a humble bacterium make this evolutionary leap from a simple prokaryotic cell to a more complex eukaryotic cell. Evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 1.
DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms is the acid that carries genetic information. The answer seems to be symbiosis in other words teamwork. Two proposed pathways describe the invasion of prokaryote cells by two smaller prokaryote cells.
The currently accepted theory of cell evolution is called the Endosymbiotic Theory. They subsequently became successfully included as part of a now much larger cell with additional structures and capable of additional functions. Most single celled organisms have a cell wall around their plasma membranes in order to protect them from.
The first cells and organisms to evolve would be classified as prokaryotic. Lewiss Medical-Surgical Nursing Diane Brown. Share this document with a friend.
A domain is the highest taxon just above the kingdom.
Popular Posts
-
Most of the agricultural societywas largely supported by the feudal system social hierarchy. The Feudal System was introduced to England fol...
-
Indian National Congress 1885. N the official name for Congress3 Collins English Dictionary Complete and Unabridged 12th Edition 2014 Harper...
-
He ruled from 5 April 1462 to 27 October 1505 he was known as Ivan the Great and was a Grand Prince of Moscow. 29 October 1603 Moscow Russia...
Featured Post
eyes but cannot see verse
83 Bible Verses about Have Eyes But Do Not See . “Son of man, you dwell in the midst of a rebellious house, who have eyes to see, but ...

ads
